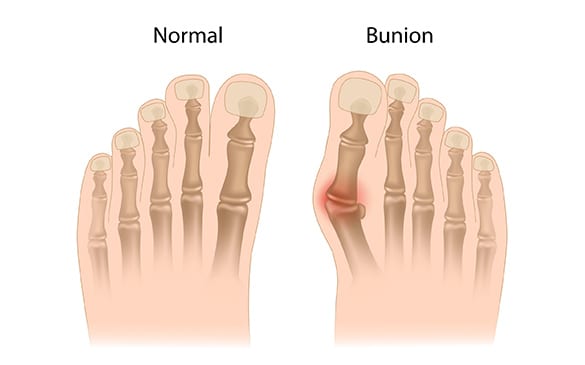
Find out how LA Orthopedic Group can help you find lasting relief from Bunions.
Often slow to develop, bunions (hallux valgus) are bony lumps that typically form on the inside of big toes. The pressure placed on the second toe may eventually lead to a misalignment or deformity that can become extensive enough to make it difficult to walk or wear shoes comfortably.
- Bunions are more common in women, especially those who wear tight-fitting shoes
- Treatment depends on the extent of the deformity and how it progresses with time
CONTACT US TODAY
How Bunions Progress
The deformity itself is initially small and may produce no noticeable discomfort at first. Calluses sometimes develop from friction produced against the skin where the bunion is located while walking, jogging, or running. The big toe could eventually move over or under the adjacent toe as the deformity progresses. Other signs of bunions include:
- A bulge on the big toe that slowly gets larger
- Swelling or redness around the big toe
- Limited movement of the big toe
- Pain that develops when wearing shoes or when moving the toe in certain positions
Foot Problems Related to Bunions
Bunions may eventually lead to other foot problems such as bursitis, an inflammation of fluid-filled sacs that cushion joints. If bunions advance far enough, joints and soft tissues in the foot may become irritated or stretched.
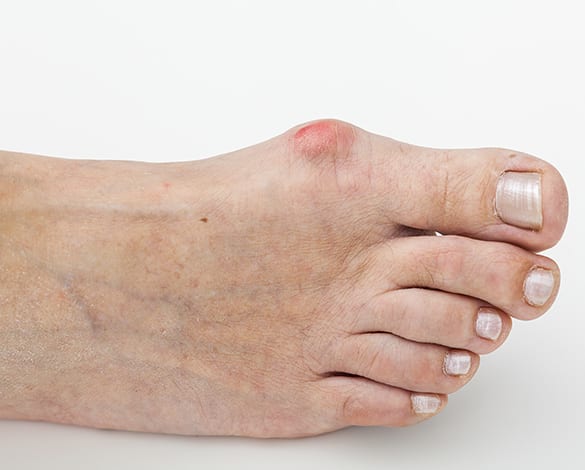

Diagnosing Bunions
Bunions are diagnosed with an examination of the visible deformity. An X-ray of the foot may be ordered to determine what may have caused the bunion and whether or not there are other issues involved with the affected toe. Additional image tests may be done if other tissue damage is suspected.
Available Treatments
Naproxen and other anti-inflammatory medications can ease related swelling. Additional medications may be prescribed if bunion pain is being aggravated by arthritis or diabetes. Some patients also benefit from protective bunion pads, custom orthotics like shoe inserts, and the application of ice for about 15-20 minutes at a time, although ice should not be directly applied to skin.
Considering Surgery
Surgery becomes a consideration for bunions if other treatments are not providing lasting relief, pain is severe, or the abnormality of the big toe has progressed to the point where no other options are available. Procedures performed often involve the realignment of the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint or the correction of problems with affected ligaments, tendons, or nerves to restore the normal functioning of the big toe. Surgery is not recommended for adolescents with bunions since bones are still developing during this time.
The risk of developing bunions can be minimized by wearing roomy shoes or choosing shoes that have about a thumb’s width of space between the big toe and top of the shoe. Also, avoid narrow shoes and high-heels as much as possible, have your feet measured regularly to make sure you are getting a proper fit, and try before you buy since shoes of the same size don’t always fit the same. If you do notice a bunion developing, be mindful of how it progresses and consider seeing an orthopedic surgeon if it becomes painful.