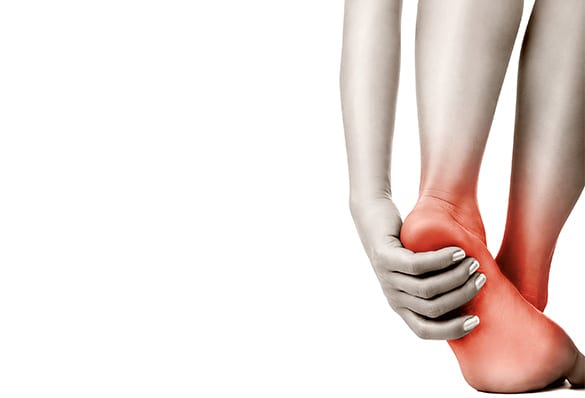
LA Orthopedic Group can provide minimally invasive treatment options for Achilles Tendonitis.
Achilles tendonitis is a type of overuse injury that is common among professional and amateur athletes. It occurs when the Achilles tendon that connects the calf muscles to the heel of the foot becomes inflamed.
- If the condition occurs in the middle portion of the tendon, it is referred to as noninsertional Achilles tendonitis
- Inflammation occurring where the tendon attaches to the heel bone is called insertional Achilles tendonitis
CONTACT US TODAY
Causes of Achilles Tendonitis
Achilles tendonitis is the result of repetitive stress or pushing the body beyond its current limits. Some factors that may increase your risk of developing Achilles tendonitis include:
- Significantly increasing the intensity or duration of your workout without giving your body time to adjust
- Not taking the time to stretch the calf muscles before starting an aggressive workout routine
- Bone spurs on the heel that rub against the tendon
Risk Factors for Achilles Tendonitis
Achilles tendonitis is most common in individuals who participate in sports that require sudden acceleration, deceleration, or pivoting, including running, tennis, gymnastics, football, and basketball. Other risk factors include:
- Being middle-aged and male
- Having flat feet
- Wearing worn athletic shoes
- Wearing high heels
- Taking certain antibiotics or glucocorticoids

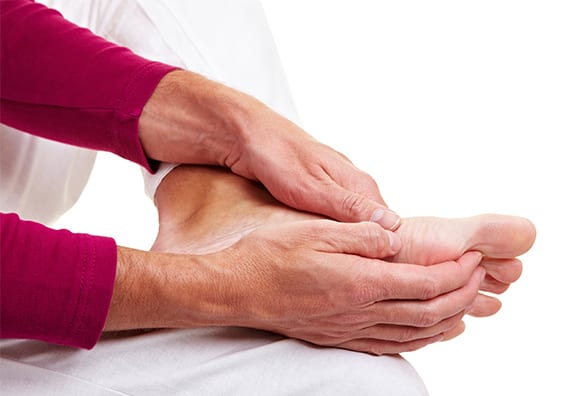
Symptoms of Achilles Tendonitis
Individuals with Achilles tendonitis typically experience stiffness along the tendon first thing in the morning that may improve after the tendon stretches with mild activity; however, the pain will normally return and worsen with intense activity. The tendon may become visibly swollen throughout the day and tender to the point that it becomes difficult to flex the foot. Since the inflammation weakens the tendon and makes it susceptible to rupture, it is important not to ignore symptoms of Achilles tendonitis and to consult a medical professional as soon as possible.
Diagnosing Achilles Tendonitis
During the physical exam, the doctor will check for swelling, tenderness, and thickening of the Achilles tendon along with a decrease in the range of motion of the ankle. X-rays, ultrasounds, and MRIs may be used to rule out other conditions involving the joints, tendons, and muscles.
Treatments for Achilles Tendonitis
Most cases of Achilles tendonitis can be resolved with conservative treatments, including:
- Rest
- Ice therapy
- Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications
- Exercise and physical therapy
- Cortisone injections
- Orthotic shoe inserts
If the tendonitis does not resolve after six months of conservative therapies, surgery may necessary to relieve the stress on the tendon and correct any damage.