Our knee doctor can determine the best treatment option for you.
While there are factors that make some people more susceptible to knee pain than other individuals, it’s something that can affect anyone at any age. The human body is fairly resilient, so much so that many instances of knee-related pain are nothing more than a temporary inconvenience.
- Self-care that involves rest, applying ice, compression, elevation, and over-the-counter NSAIDs like ibuprofen often relieve knee pain from relatively minor issues.
- It’s when treatments like these aren’t effective, or when symptoms linger and mobility and stability are affected, that’s time to consider a visit to a knee doctor in Los Angeles.
CONTACT US TODAY
Making an Accurate Diagnosis
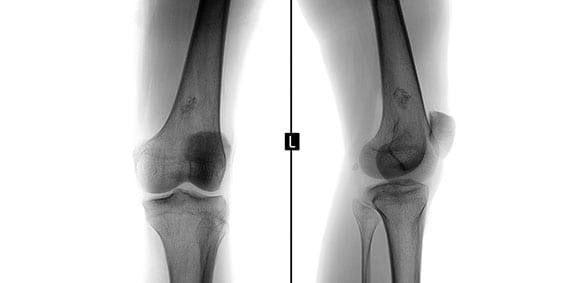
From sudden, acute injuries—like what may happen following a sports injury or hard fall—to mechanical problems involving loose bone or cartilage, dislocation, or a torn meniscus or ACL (anterior cruciate ligament), there are many possible sources of knee issues. Following an initial exam and visual inspection to look for swelling and signs of injury, a review of symptoms, and a discussion of a patient’s previous attempts at relief, your knee doctor in Los Angeles typically orders X-rays and other image tests to make a more accurate diagnosis. Lab tests may be done if gout or an infection like septic arthritis is suspected. Fluid is also sometimes removed from the knee joint (arthrocentesis) for analysis.

Recommending Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Other than results from tests, treatments recommended by a knee doctor in Los Angeles will depend on factors such as a patient’s normal activity level and pain management goals. In many cases, non-surgical treatment options are recommended first. When knee pain is affected by rheumatoid arthritis or another underlying health issues, NSAIDs may minimize tissue swelling. Acetaminophen sometimes eases mild discomfort, while topical creams, gels, or patches may reduce amounts of chemicals that help transmit signals to the part of the brain that interprets pain.
If oral or topical medications don’t provide sufficient relief, a knee doctor may suggest corticosteroid or hyaluronic acid injections that are placed directly into the affected part of the knee. Patients looking to promote tissue healing may benefit from platelet-rich plasma injections. Prepared with parts of a patient’s own blood, PRP injections contain higher concentrations of special growth factors that help tissues heal. Injections of this nature are often recommended for younger and otherwise healthy patients. With knee pain due to fractures, treatment may involve temporary bracing or casting if the broken bone is still in its correct position. Ligament and tendon tears that aren’t severe may respond well to the RICE method (rest, ice, compression, elevation) or medication that eases swelling. Physical therapy can also help strengthen muscles around the knee to improve stability.
Considering Knee Surgery
Even when surgery becomes part of the discussion, it’s rarely immediately necessary. Yet there are times when surgery is the only available option, as may be the case if the collateral ligament that connects the femur to the tibia is completely detached or if a kneecap has shifted significantly out of place. For some knee problems, it may be possible to correct damage with arthroscopic surgery performed with a fiber-optic camera and special instruments. Partial and total knee replacements are often able to be completed successfully if other treatments aren’t providing sufficient relief.
Preventing Knee Injuries and Pain
Being involved with contact sports, not properly warming up before running or jogging, excess weight, and a lack of muscle flexibility or strength are among the factors that can contribute to knee problems. It’s not entirely possible to prevent everything that may cause knee pain. However, there are steps that can be taken to reduce injury risks. If, for example, you have osteoarthritis (OA), you might consider water-based exercises or modifying activities to avoid excessive pressure on the three bones that form your knee joint or the supporting soft tissues. Your knee doctor in Los Angeles may also suggest preventative efforts that include:
- Adhering to proper form while playing sports or exercising
- Incorporating green, leafy vegetables, whole grains, and other foods that naturally control inflammation into your diet
- Avoiding sudden changes in exercise or workout routines
Immediate attention should be sought if knees are producing severe pain, visibly swollen, clearly deformed, or if a popping noise was heard when the injury occurred. Your knee doctor in Los Angeles can also provide input for patients with knee issues that will eventually require some decisions to be made involving surgery. A common example of this is athletes living with ligament or tendon problems weighing their treatment options. Surgery is often a last resort for most sources of knee pain or instability. Fortunately, there are many minimally invasive procedures that may restore full function without the need for a lengthy recovery process.